Table of Contents
ToggleBrief overview of ocean life and its significance
The ocean, covering over 70% of Earth’s surface, is home to a vast array of life forms, from microscopic plankton to the colossal blue whale. This diverse ecosystem plays a crucial role in maintaining the planet’s health, regulating climate, and supporting a wide variety of marine species.
Marine life contributes to the oxygen we breathe, with phytoplankton alone producing about 50% of the world’s oxygen. Oceans also serve as a major food source and support global economies through fishing and tourism.
The intricate web of life beneath the waves, including coral reefs, kelp forests, and deep-sea trenches, showcases an incredible variety of adaptations and behaviors.
Understanding and preserving ocean life is essential, not just for the creatures that inhabit these waters, but for the overall health and sustainability of our planet. Protecting these ecosystems ensures the continuation of the vital services they provide to humanity and the natural world.
Types of Marine Life
What are the Three Types of Marine Life?
Marine life can be categorized into three main types: plankton, nekton, and benthos.
Plankton are tiny, often microscopic organisms that drift with ocean currents. They form the base of the marine food web and include phytoplankton, which are photosynthetic, and zooplankton, which feed on phytoplankton and other zooplankton.
Nekton are active swimmers capable of moving independently of water currents. This group includes a wide range of animals, from small fish to large marine mammals like dolphins and whales. Nektonic creatures are crucial predators and prey within their ecosystems.
Benthos live on or near the ocean floor. This diverse group includes organisms like crabs, starfish, and sea anemones, as well as bottom-dwelling fish. Benthos play a vital role in nutrient cycling and are key to maintaining the health of marine ecosystems. Understanding these categories helps us appreciate the complexity and interdependence of ocean life.
Common Marine Life
The ocean is teeming with life, and some of the most common species are essential to marine ecosystems.
Phytoplankton, microscopic plants, form the foundation of the oceanic food web, producing oxygen and serving as food for many marine animals. Zooplankton, tiny drifting animals, feed on phytoplankton and provide sustenance for larger species.
Among larger marine life, fish are incredibly diverse and widespread.
Clownfish, known for their vibrant colors and symbiotic relationship with sea anemones, are a familiar sight in coral reefs. Anchovies and sardines are small, schooling fish vital to the diets of many larger predators.
Marine mammals like dolphins and whales are also common and play significant roles in their habitats. Sea turtles, found in oceans worldwide, contribute to marine biodiversity by maintaining healthy seagrass beds and coral reefs.
These species, among many others, highlight the ocean’s rich and varied life forms.

Exploring the Ocean’s Inhabitants
What Kind of Life Lives in the Ocean?
The ocean is a vast and diverse environment, home to a multitude of habitats, each with its unique inhabitants. Coral reefs, often referred to as the “rainforests of the sea,” are bustling with life, including colorful fish like clownfish, vibrant corals, sponges, and sea anemones. These ecosystems provide shelter and food for a myriad of marine species.
Kelp forests, found in cooler coastal waters, are dominated by large, brown seaweeds known as kelp. These underwater forests are habitats for species like sea otters, abalones, and various fish, offering both food and protection.
Open ocean, or pelagic zone, is home to nektonic animals such as sharks, tuna, dolphins, and whales. This vast, open-water environment supports species that are often migratory and capable of traveling long distances.
Deep-sea environments, including abyssal plains and hydrothermal vents, host unique and often bizarre creatures adapted to extreme conditions. Bioluminescent fish, giant tube worms, and deep-sea squids are examples of life forms that thrive in these dark, high-pressure habitats.
Polar regions feature cold, nutrient-rich waters inhabited by species like krill, polar bears, and seals. These areas are crucial for many migratory species, including whales and seabirds, that rely on the abundant food sources.
Each of these habitats supports a distinct community of marine life, showcasing the ocean’s incredible biodiversity.
Sea Creatures Information and List
The ocean is home to a remarkable diversity of sea creatures, ranging from common to rare and even unknown species. Here is a comprehensive list highlighting some of these fascinating beings:
Common Sea Creatures:
– Clownfish: Known for their bright colors and symbiotic relationship with sea anemones.
– Dolphins: Intelligent and social marine mammals found in oceans worldwide.
– Jellyfish: Gelatinous creatures that drift through the water, some with painful stings.
– Sea Turtles: Ancient reptiles known for their long migrations and diverse habitats.
Rare Sea Creatures:
– Coelacanth: A prehistoric fish once thought to be extinct, found in deep waters.
– Giant Squid: Elusive deep-sea dwellers, rarely seen by humans.
– Vaquita: The world’s rarest marine mammal, critically endangered and found in the Gulf of California.
– Dumbo Octopus: A deep-sea octopus named for its ear-like fins that resemble those of Disney’s Dumbo.
Unknown or Lesser-Known Sea Creatures:
– Yeti Crab: Discovered near hydrothermal vents, known for its hairy claws.
– Barreleye Fish: Deep-sea fish with a transparent head and tubular eyes.
– Goblin Shark: A rare, deep-sea shark with a distinctive protruding snout and nail-like teeth.
– Sea Pig: A type of sea cucumber found on the ocean floor, notable for its unusual appearance.
These examples illustrate the incredible variety of marine life, from the familiar to the mysterious, highlighting the ocean’s rich biodiversity and the ongoing discovery of new species.
What are the Top 5 Animals That Live Under the Sea?
The ocean is home to countless fascinating creatures, but five stand out for their unique characteristics and intriguing behaviors:
1. Great White Shark: Known for its size and power, this apex predator is crucial for maintaining marine ecosystem balance.
2. Blue Whale: The largest animal on Earth, blue whales can grow up to 100 feet long and weigh as much as 200 tons.
3. Octopus: Highly intelligent and adaptable, octopuses are known for their problem-solving skills, ability to camouflage, and escape artistry.
4. Manta Ray: These graceful giants glide through the ocean with wing-like pectoral fins, often seen “flying” underwater.
5. Sea Turtle: Ancient mariners of the ocean, sea turtles travel thousands of miles across seas, playing essential roles in marine ecosystems by maintaining healthy seagrass beds and coral reefs.
These five sea creatures exemplify the diversity and wonder of marine life, each contributing uniquely to the ocean’s rich tapestry.

Amazing and Bizarre Ocean Creatures
What is the Most Amazing Sea Creature?
The ocean is filled with astonishing creatures, but the mantis shrimp stands out as one of the most amazing. Known for its incredible speed and power, the mantis shrimp can strike with the speed of a bullet, capable of breaking glass and crushing crabs’ shells. Beyond its physical prowess, the mantis shrimp boasts the most complex eyes in the animal kingdom, with 16 color-receptive cones compared to humans’ three, allowing it to see a vast range of colors and polarized light.
Other remarkable sea creatures include the blue dragon (Glaucus atlanticus), a stunningly beautiful sea slug that floats on the ocean surface and preys on venomous jellyfish, storing their stinging cells for its defense. The giant squid, with eyes the size of dinner plates, navigates the deep sea in near-total darkness. Lastly, the immortal jellyfish (Turritopsis dohrnii) can revert to its juvenile form after reaching maturity, potentially living forever.
What is the Most Bizarre Ocean Creature?
The blobfish (Psychrolutes marcidus) is often considered the most bizarre ocean creature due to its unusual appearance. Found in the deep waters off the coasts of Australia and New Zealand, the blobfish has a gelatinous, droopy appearance when brought to the surface, earning it the title of the “world’s ugliest animal.” This strange look is due to the lack of muscle and a low-density body, which allows it to withstand the extreme pressure of its deep-sea habitat.
Another bizarre creature is the anglerfish, known for the bioluminescent lure on its head used to attract prey in the dark depths of the ocean.
The gulper eel, with its enormous, expandable mouth, can swallow prey much larger than itself. The hatchetfish, with its eerie, metallic sheen and upward-facing eyes, is adapted for life in the deep, dark ocean, using bioluminescence to camouflage itself.
What is the Most Rare Sea Creature?
The coelacanth (Latimeria chalumnae) is often considered one of the rarest sea creatures. Once thought to be extinct for millions of years until a living specimen was discovered off the coast of South Africa in 1938, coelacanths are ancient fish with a unique evolutionary history. These “living fossils” inhabit deep-sea caves and are rarely encountered by humans due to their elusive nature and inaccessible habitats.
Another rare sea creature is the Irrawaddy dolphin (Orcaella brevirostris), found in coastal areas and rivers of Southeast Asia. With a distinctive rounded forehead and lack of beak, these dolphins are highly endangered due to habitat loss, pollution, and entanglement in fishing gear.
The spotted wobbegong shark (Orectolobus maculatus) is also considered rare due to its cryptic camouflage and nocturnal habits.
These bottom-dwelling sharks are native to the waters of Australia and Indonesia and are rarely seen by humans unless specifically sought out by divers or researchers.

The Importance of Ocean Life
Why is Ocean Life Important?
Ocean life is vital for sustaining Earth’s ecosystems, economies, and cultures. Ecologically, marine organisms contribute to oxygen production, carbon sequestration, and nutrient cycling, regulating the planet’s climate and maintaining biodiversity. Economically, oceans support industries such as fishing, shipping, tourism, and pharmaceuticals, providing livelihoods for millions of people worldwide. Additionally, marine ecosystems generate valuable services like coastal protection and water filtration, benefiting coastal communities and beyond.
Culturally, oceans hold deep significance for coastal societies, providing food, inspiration for art and literature, and spiritual connections. Indigenous communities often have intricate relationships with marine life, relying on it for cultural practices, traditions, and identities. Protecting ocean life is essential not only for ecological balance but also for ensuring sustainable livelihoods and preserving cultural heritage for future generations.
Why is Underwater Life Important?
Underwater life is crucial for maintaining the health and stability of the global ecosystem. Marine organisms play key roles in nutrient cycling, carbon sequestration, and regulating Earth’s climate. Phytoplankton, for example, produce around 50% of the world’s oxygen through photosynthesis, while also absorbing significant amounts of atmospheric carbon dioxide.
Additionally, marine life forms the base of the oceanic food web, supporting higher trophic levels such as fish, marine mammals, and seabirds. Healthy marine ecosystems provide essential services like coastal protection, storm buffering, and water filtration, benefiting both human societies and terrestrial environments.
Furthermore, underwater life contributes to biodiversity, genetic diversity, and evolutionary processes, enhancing resilience to environmental changes.
Protecting and preserving underwater life is essential for sustaining Earth’s ecosystems, ensuring food security, and mitigating the impacts of climate change on both land and sea.

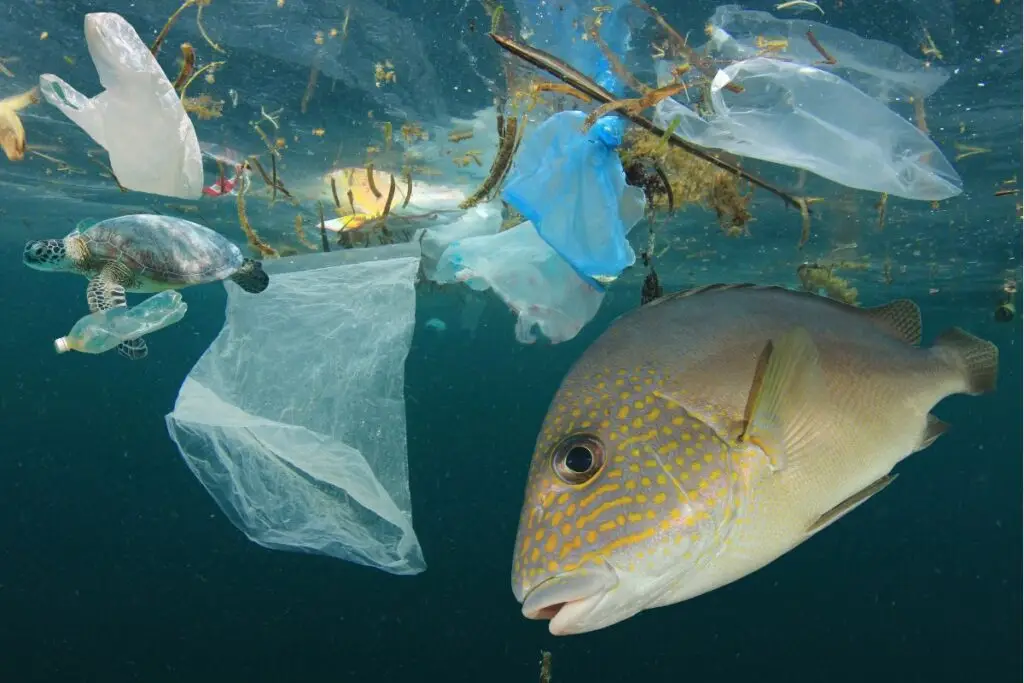
Threats to Marine Life
How is Marine Life in Danger?
Marine life faces numerous threats, primarily driven by human activities. Overfishing and destructive fishing practices, such as bottom trawling and bycatch, deplete fish populations and damage marine habitats.
Pollution, including plastic waste, chemical runoff, and oil spills, contaminates marine environments, harming marine species and ecosystems.
Climate change exacerbates these threats, leading to ocean acidification, rising sea temperatures, and coral bleaching, which devastate coral reefs and marine habitats. Habitat destruction from coastal development, dredging, and coral mining further diminishes suitable habitats for marine life.
Invasive species introduce competition, predation, and disease, disrupting native ecosystems and threatening indigenous species. Additionally, illegal wildlife trade, including the poaching of marine mammals, sea turtles, and endangered species, contributes to population declines and biodiversity loss.
Addressing these threats requires international cooperation, sustainable fisheries management, marine protected areas, pollution reduction measures, and climate change mitigation strategies. Protecting marine ecosystems is crucial for safeguarding biodiversity, maintaining ecosystem services, and ensuring the long-term health and resilience of the ocean and its inhabitants.
What is Happening to Ocean Life?
Ocean life faces significant challenges due to human activities and environmental changes. Marine ecosystems are experiencing declines in biodiversity, with species populations plummeting due to overfishing, habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change. Coral reefs, often referred to as the “rainforests of the sea,” are particularly vulnerable, facing widespread bleaching events and degradation from rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification.
Conservation efforts are underway to address these issues, including the establishment of marine protected areas, sustainable fisheries management, and initiatives to reduce plastic pollution and carbon emissions. Scientists, policymakers, and conservation organizations collaborate to monitor marine ecosystems, conduct research, and implement conservation strategies aimed at restoring and preserving ocean health.
Despite these efforts, the challenges facing ocean life remain immense, requiring global cooperation and concerted action to mitigate threats and promote sustainable practices. Public awareness, education, and advocacy play crucial roles in fostering a greater understanding of the importance of ocean conservation and inspiring collective action to protect marine ecosystems for future generations.
Is it OK to Touch Marine Life?
Interacting with marine life should be approached with caution and responsibility to minimize harm to both the animals and their habitats. Generally, it is not advisable to touch marine creatures in their natural environments. Touching can disrupt their behavior, damage delicate skin or structures, and introduce stress or disease.
If you encounter marine life while snorkeling, diving, or exploring tide pools, maintain a respectful distance and observe without touching. Avoid handling or disturbing animals, especially corals, sea turtles, and other protected species. Adhere to local regulations and guidelines, and seek guidance from trained professionals or naturalists when encountering marine life in controlled settings like aquariums or wildlife tours.
Responsible interaction ensures the safety and well-being of marine creatures while preserving the integrity of their ecosystems for future generations to enjoy and appreciate.

Fun and Educational Resources
Ocean Life Facts
Ocean life is filled with fascinating facts that highlight the diversity, resilience, and wonder of marine creatures and their habitats:
1. Bioluminescent Wonders: Many marine organisms, such as firefly squid and deep-sea anglerfish, produce their light through bioluminescence, used for communication, camouflage, and attracting prey.
2. Giant’s Realm: The blue whale, Earth’s largest animal, can grow up to 100 feet long and weigh as much as 200 tons, dwarfing any other creature on the planet.
3. Coral Cities: Coral reefs are home to over a quarter of all marine species, despite covering less than 1% of the ocean floor. These vibrant ecosystems provide critical habitats, nurseries, and food sources for countless marine organisms.
4. Oceanic Nomads: Some species of sea turtles, like the loggerhead and leatherback, migrate thousands of miles between nesting and feeding grounds, relying on Earth’s magnetic fields and ocean currents for navigation.
5. Underwater Architects: Pufferfish are known for their intricate, circular sand nests, created to attract mates. These underwater masterpieces can span several feet in diameter and are meticulously crafted with their fins and mouths.
These facts offer just a glimpse into the captivating world of ocean life, showcasing the marvels and mysteries that abound beneath the waves.
Ocean Life Drawings and Coloring Books
Introducing the Creatures of the Sea Coloring Book for Adults: Relax and Learn—a captivating educational tool that immerses you in the mesmerizing world of oceanic creatures. With 38 exquisite illustrations featuring a diverse array of marine life, including Barracuda Fish, Dolphin, Jellyfish, Octopus, and Stingray, this coloring book invites you to unleash your creativity and bring these fascinating creatures to life on paper.
Each intricate design, inspired by the art of zentangle and mandalas, offers a delightful blend of relaxation and education, making it perfect for adults of all skill levels. Accompanying each illustration are intriguing facts that offer deeper insights into the animals’ habitats, behaviors, and unique features, enhancing your understanding of the ocean’s wonders.
Designed with convenience and aesthetic appeal, this coloring book features a glossy cover for added durability is an ideal gift for ocean enthusiasts, animal lovers, or anyone needing a calming activity.
Embark on a journey to the depths of the sea as you engage your mind, soothe your soul, and lose yourself in the sea’s intricate patterns and soothing colors. Order your copy today and start coloring your way to inner peace and relaxation!
Tips for Coloring the Sea Creatures Illustrations
Coloring sea creature illustrations can be a delightful and relaxing activity. Here are some tips to make your coloring experience more enjoyable:
1. Reference Photos: Refer to real-life images of sea creatures for accurate color inspiration.
2. Layering Technique: Start with lighter colors as a base layer and gradually build up darker shades for depth and dimension.
3. Blending Colors: Experiment with blending colors together to create smooth transitions and realistic effects.
4. Highlighting and Shading: Add highlights with lighter shades and shadows with darker hues to create contrast and realism.
5. Texture Effects: Use different coloring techniques such as stippling, cross-hatching, or scumbling to create texture and detail.
6. Creative Freedom: Don’t be afraid to get creative and add your own artistic flair to the illustrations. Let your imagination guide you as you bring these sea creatures to life with vibrant colors and imaginative patterns.
With these tips in mind, you can turn each illustration into a masterpiece filled with beauty and vibrancy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ocean Life Definition
Ocean life refers to the diverse array of living organisms that inhabit the Earth’s oceans and seas. This includes a wide range of species, from microscopic plankton to massive marine mammals. Ocean life encompasses various habitats, from the sunlit surface waters to the dark depths of the abyssal zone.
Key components of ocean life include:
– Phytoplankton and zooplankton, which form the base of the marine food web.
– Nektonic organisms like fish, marine mammals, and squid that are capable of swimming against ocean currents.
– Benthic organisms such as coral reefs, seagrasses, and bottom-dwelling creatures that inhabit the ocean floor.
How Much Life is Underwater?
The underwater world is teeming with life, boasting an astonishing diversity of species. While exact numbers are difficult to determine due to the vastness and complexity of marine ecosystems, scientists estimate that there may be millions of species yet to be discovered in the oceans.
Current data suggests that marine biodiversity is exceptionally high, with marine environments supporting roughly 80% of all life on Earth. For example, coral reefs, covering less than 1% of the ocean floor, are estimated to host over a quarter of all marine species. Additionally, marine ecosystems like estuaries, mangroves, and deep-sea vents harbor unique and specialized organisms.
Despite the challenges of exploring and studying the ocean depths, ongoing research efforts continue to uncover new species and expand our understanding of marine biodiversity. Protecting these diverse ecosystems is critical for preserving the wealth of life underwater and ensuring the health and resilience of marine environments for future generations.
Is There Intelligent Life Underwater?
Intelligence in marine life is a fascinating subject that challenges traditional definitions and perceptions of cognition. While underwater environments may not foster intelligence in the same way as terrestrial habitats, there are indeed examples of remarkable cognitive abilities among certain marine species.
One notable example is the cephalopod family, which includes octopuses, cuttlefish, and squid. These creatures exhibit advanced problem-solving skills, complex social behaviors, and remarkable camouflage abilities. Octopuses, in particular, are renowned for their ability to manipulate objects, solve puzzles, and even display play behavior, suggesting a high level of cognitive sophistication.
Dolphins are another well-known example of intelligent marine life. These cetaceans demonstrate complex communication systems, social structures, and tool use. They exhibit self-awareness, as demonstrated by their ability to recognize themselves in mirrors, a trait previously thought to be unique to humans and great apes.
Whales also display signs of intelligence, with some species exhibiting intricate hunting strategies, cultural behaviors, and long-term social bonds.
While these examples showcase impressive cognitive abilities, the concept of intelligence in marine life remains a subject of ongoing research and debate. Understanding the cognitive capacities of marine species can provide valuable insights into the evolution of intelligence and consciousness across diverse ecosystems.
What is the Deadliest Sea Creature Ever?
Determining the “deadliest” sea creature is challenging as it depends on various factors such as toxicity, aggression, and human interactions. However, several marine species are known for their dangerous capabilities:
1. Box Jellyfish (Chironex fleckeri): Found in the waters of the Indo-Pacific region, the box jellyfish is one of the most venomous creatures in the world. Its tentacles contain toxins that can cause severe pain, cardiac arrest, and even death in humans.
2. Blue-Ringed Octopus (Hapalochlaena spp.): Despite its small size, the blue-ringed octopus carries potent neurotoxins that can cause paralysis and respiratory failure. Encounters with this octopus are rare but potentially fatal.
3. Saltwater Crocodile (Crocodylus porosus): Often found in coastal regions of Southeast Asia and Australia, saltwater crocodiles are apex predators capable of attacking and killing humans with their powerful jaws and hunting prowess.
4. Great White Shark (Carcharodon carcharias): While attacks on humans are rare, great white sharks are known for their formidable size, strength, and predatory behavior, making them one of the ocean’s most feared creatures.
While these species are considered dangerous, it’s important to remember that most marine encounters are non-threatening. Understanding and respecting marine life, as well as adhering to safety guidelines, can help mitigate the risks associated with ocean activities.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the ocean is not only a vast expanse of water but also a rich and vital ecosystem teeming with life. From the smallest plankton to the largest whales, marine organisms play crucial roles in regulating Earth’s climate, supporting global fisheries, and providing valuable ecosystem services.
As stewards of our planet, it’s essential to recognize the importance of ocean life and the urgent need to protect and preserve marine environments. By understanding the interconnectedness of marine ecosystems and the impact of human activities, we can work towards sustainable practices that ensure the health and resilience of our oceans for future generations.
One way to learn more about sea creatures and their habitats is through the Creatures of the Sea Coloring Book for Adults: Relax and Learn.
With 38 exquisite illustrations and intriguing facts accompanying each design, this coloring book offers a delightful blend of relaxation and education. Immerse yourself in the captivating realm of oceanic creatures, unleash your creativity, and explore the wonders of the sea through vibrant colors and intricate patterns.
Order your copy today and embark on a journey to the depths of the sea.
Let the vibrant hues of the ocean wash away your worries and awaken your senses to the beauty and serenity that lie beneath the surface. Together, let’s celebrate and protect the magnificent diversity of ocean life.